
Any signs of bleeding must be noted and reported to the physician in order to be addressed immediately. Double check the dosage before administration to be ensure that it is the correct dose. The primary way to prevent heparin overdose is to take the drug as instructed by the physician. Due to the severity of anaphylactic reaction to protamine, anaphylactic treatment and resuscitation equipment must be on standby when giving this drug. The side effects associated to taking protamine include hypotension and anaphylaxis reaction. The drug required to counteract heparin reduces over time as the body starts to metabolize heparin. If an individual experiences bleeding due to an increased level of heparin in the blood, the drug protamine sulfate may be given by slow infusion.ġmg of protamine sulfate is needed to neutralize 100 units of heparin although the maximum amount that can be given in a 10-minute period is 50mg. The presence of unexplained bruises or petechial formations may indicate the possibility of frank bleeding. These are just the initial signs of bleeding in the patient. There may even be nosebleeds and the presence of blood in the urine.
The patient will experience GI bleeding as evidenced by vomiting of blood or appearance of tarry or black stools. The main symptom of an heparin overdose is the occurrence of bleeding. A person is considered to overdose on heparin if their ability to form blood clots is impaired. The bleeding time of the patient is the basis for the toxicity.

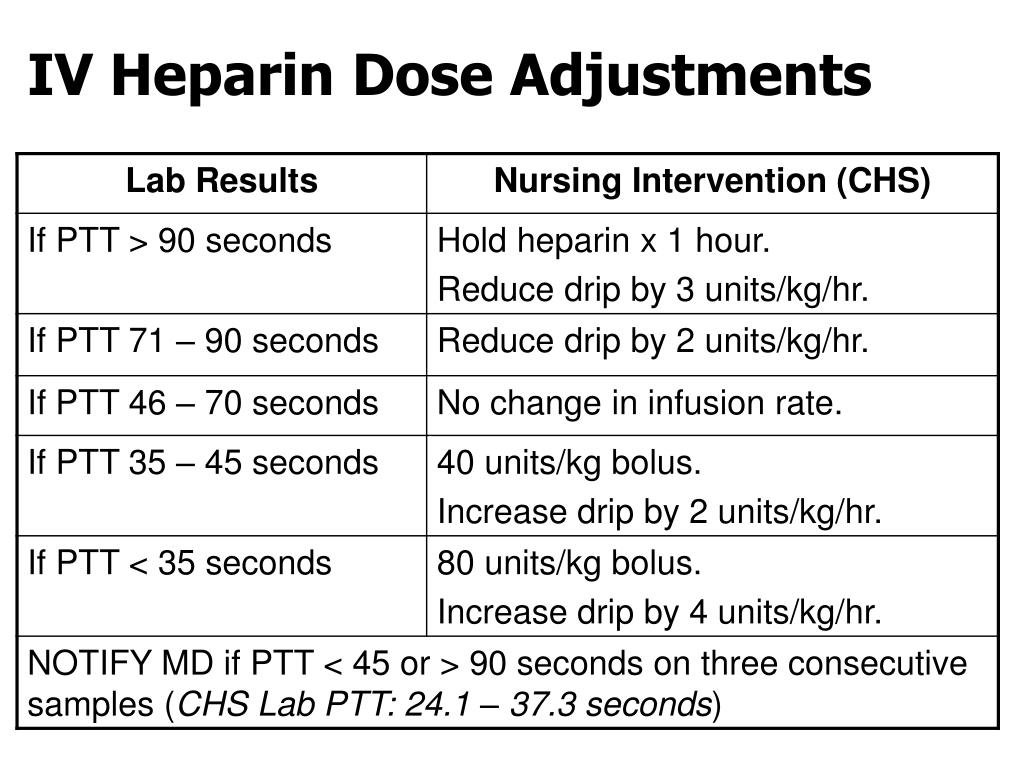
The amount of heparin that is toxic to individuals depend from one individual to another. The bleeding time of patients who take this medication are monitored because there may be a need to adjust the dosage of the drug depending on the results of these tests.
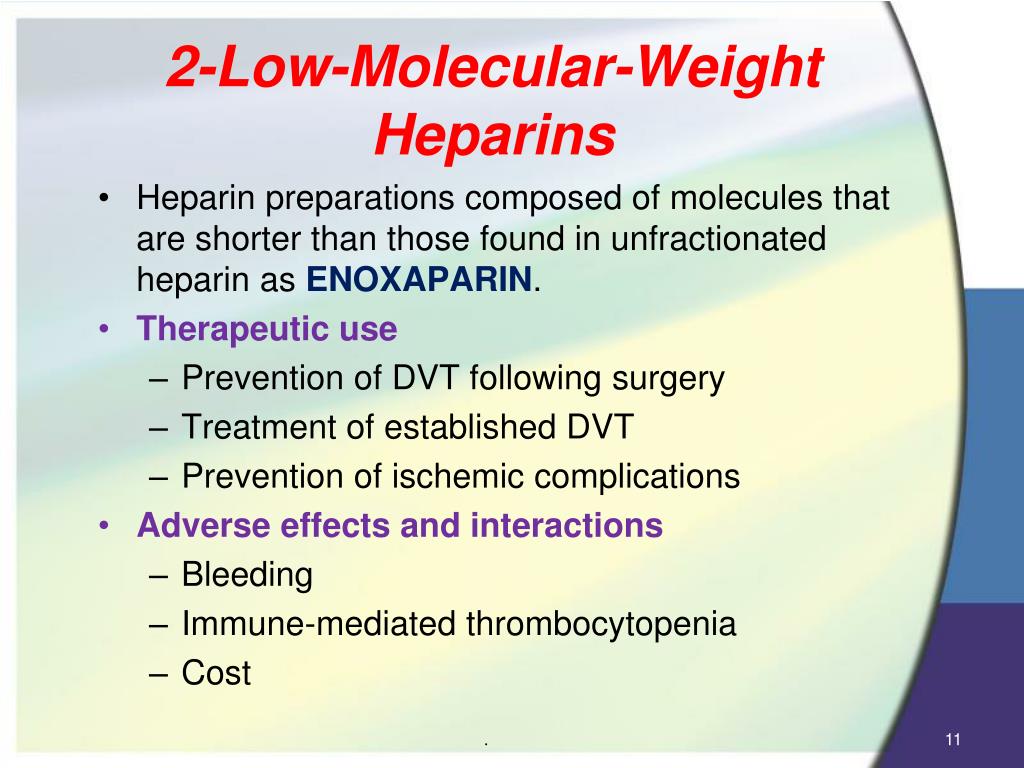
The physician must be advised once signs of bleeding such as easy bruising, presence of black, tarry stools, nosebleed, blood in the urine or any bleeding that fails to stop. One of the potential side effects of taking this drug is the possibility of bleeding. It is also used to maintain the patency of intravenous catheters or as a lock flush. Heparin is usually given to patients who will undergo a surgical procedure to decrease the chance of clotting. The main function of heparin is to prevent the conversion of clotting factors to avoid the formation of blood clots.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
